In Tuesday’s State of the Union address, the President touched on many important issues facing our country. To learn more about those issues, we are pleased to offer authoritative resources from the National Academies in the areas of public policy, science, engineering, and medicine.
Remarks of President Barack Obama in State of the Union Address
Mr. Speaker, Mr. Vice President, Members of Congress, distinguished guests, and fellow Americans:
Tonight I want to begin by congratulating the men and women of the 112th Congress, as well as your new Speaker, John Boehner. And as we mark this occasion, we are also mindful of the empty chair in this Chamber, and pray for the health of our colleague – and our friend – Gabby Giffords.
It’s no secret that those of us here tonight have had our differences over the last two years. The debates have been contentious; we have fought fiercely for our beliefs. And that’s a good thing. That’s what a robust democracy demands. That’s what helps set us apart as a nation.
But there’s a reason the tragedy in Tucson gave us pause. Amid all the noise and passions and rancor of our public debate, Tucson reminded us that no matter who we are or where we come from, each of us is a part of something greater – something more consequential than party or political preference.
We are part of the American family. We believe that in a country where every race and faith and point of view can be found, we are still bound together as one people; that we share common hopes and a common creed; that the dreams of a little girl in Tucson are not so different than those of our own children, and that they all deserve the chance to be fulfilled.
That, too, is what sets us apart as a nation.
Now, by itself, this simple recognition won’t usher in a new era of cooperation. What comes of this moment is up to us. What comes of this moment will be determined not by whether we can sit together tonight, but whether we can work together tomorrow.
I believe we can. I believe we must. That’s what the people who sent us here expect of us. With their votes, they’ve determined that governing will now be a shared responsibility between parties. New laws will only pass with support from Democrats and Republicans. We will move forward together, or not at all – for the challenges we face are bigger than party, and bigger than politics.
At stake right now is not who wins the next election – after all, we just had an election. At stake is whether new jobs and industries take root in this country, or somewhere else. It’s whether the hard work and industry of our people is rewarded. It’s whether we sustain the leadership that has made America not just a place on a map, but a light to the world.
We are poised for progress. Two years after the worst recession most of us have ever known, the stock market has come roaring back. Corporate profits are up. The economy is growing again.
But we have never measured progress by these yardsticks alone. We measure progress by the success of our people. By the jobs they can find and the quality of life those jobs offer. By the prospects of a small business owner who dreams of turning a good idea into a thriving enterprise. By the opportunities for a better life that we pass on to our children.
That’s the project the American people want us to work on. Together.
We did that in December. Thanks to the tax cuts we passed, Americans’ paychecks are a little bigger today. Every business can write off the full cost of the new investments they make this year. These steps, taken by Democrats and Republicans, will grow the economy and add to the more than one million private sector jobs created last year.
But we have more work to do. The steps we’ve taken over the last two years may have broken the back of this recession – but to win the future, we’ll need to take on challenges that have been decades in the making.
Many people watching tonight can probably remember a time when finding a good job meant showing up at a nearby factory or a business downtown. You didn’t always need a degree, and your competition was pretty much limited to your neighbors. If you worked hard, chances are you’d have a job for life, with a decent paycheck, good benefits, and the occasional promotion. Maybe you’d even have the pride of seeing your kids work at the same company.
That world has changed. And for many, the change has been painful. I’ve seen it in the shuttered windows of once booming factories, and the vacant storefronts of once busy Main Streets. I’ve heard it in the frustrations of Americans who’ve seen their paychecks dwindle or their jobs disappear – proud men and women who feel like the rules have been changed in the middle of the game.
They’re right. The rules have changed. In a single generation, revolutions in technology have transformed the way we live, work and do business. Steel mills that once needed 1,000 workers can now do the same work with 100. Today, just about any company can set up shop, hire workers, and sell their products wherever there’s an internet connection.
Meanwhile, nations like China and India realized that with some changes of their own, they could compete in this new world. And so they started educating their children earlier and longer, with greater emphasis on math and science. They’re investing in research and new technologies. Just recently, China became home to the world’s largest private solar research facility, and the world’s fastest computer.
So yes, the world has changed. The competition for jobs is real. But this shouldn’t discourage us. It should challenge us. Remember – for all the hits we’ve taken these last few years, for all the naysayers predicting our decline, America still has the largest, most prosperous economy in the world. No workers are more productive than ours. No country has more successful companies, or grants more patents to inventors and entrepreneurs. We are home to the world’s best colleges and universities, where more students come to study than any other place on Earth.
What’s more, we are the first nation to be founded for the sake of an idea – the idea that each of us deserves the chance to shape our own destiny. That is why centuries of pioneers and immigrants have risked everything to come here. It’s why our students don’t just memorize equations, but answer questions like “What do you think of that idea? What would you change about the world? What do you want to be when you grow up?”
The future is ours to win. But to get there, we can’t just stand still. As Robert Kennedy told us, “The future is not a gift. It is an achievement.” Sustaining the American Dream has never been about standing pat. It has required each generation to sacrifice, and struggle, and meet the demands of a new age.
Now it’s our turn. We know what it takes to compete for the jobs and industries of our time. We need to out-innovate, out-educate, and out-build the rest of the world. We have to make America the best place on Earth to do business. We need to take responsibility for our deficit, and reform our government. That’s how our people will prosper. That’s how we’ll win the future. And tonight, I’d like to talk about how we get there.
The first step in winning the future is encouraging American innovation.
None of us can predict with certainty what the next big industry will be, or where the new jobs will come from. Thirty years ago, we couldn’t know that something called the Internet would lead to an economic revolution. What we can do – what America does better than anyone – is spark the creativity and imagination of our people. We are the nation that put cars in driveways and computers in offices; the nation of Edison and the Wright brothers; of Google and Facebook. In America, innovation doesn’t just change our lives. It’s how we make a living.
Our free enterprise system is what drives innovation. But because it’s not always profitable for companies to invest in basic research, throughout history our government has provided cutting-edge scientists and inventors with the support that they need. That’s what planted the seeds for the Internet. That’s what helped make possible things like computer chips and GPS.
Just think of all the good jobs – from manufacturing to retail – that have come from those breakthroughs.
Half a century ago, when the Soviets beat us into space with the launch of a satellite called Sputnik¸ we had no idea how we’d beat them to the moon. The science wasn’t there yet. NASA didn’t even exist. But after investing in better research and education, we didn’t just surpass the Soviets; we unleashed a wave of innovation that created new industries and millions of new jobs.
This is our generation’s Sputnik moment. Two years ago, I said that we needed to reach a level of research and development we haven’t seen since the height of the Space Race. In a few weeks, I will be sending a budget to Congress that helps us meet that goal. We’ll invest in biomedical research, information technology, and especially clean energy technology – an investment that will strengthen our security, protect our planet, and create countless new jobs for our people.
Already, we are seeing the promise of renewable energy. Robert and Gary Allen are brothers who run a small Michigan roofing company. After September 11th, they volunteered their best roofers to help repair the Pentagon. But half of their factory went unused, and the recession hit them hard.
Today, with the help of a government loan, that empty space is being used to manufacture solar shingles that are being sold all across the country. In Robert’s words, “We reinvented ourselves.”
That’s what Americans have done for over two hundred years: reinvented ourselves. And to spur on more success stories like the Allen Brothers, we’ve begun to reinvent our energy policy. We’re not just handing out money. We’re issuing a challenge. We’re telling America’s scientists and engineers that if they assemble teams of the best minds in their fields, and focus on the hardest problems in clean energy, we’ll fund the Apollo Projects of our time.
At the California Institute of Technology, they’re developing a way to turn sunlight and water into fuel for our cars. At Oak Ridge National Laboratory, they’re using supercomputers to get a lot more power out of our nuclear facilities. With more research and incentives, we can break our dependence on oil with biofuels, and become the first country to have 1 million electric vehicles on the road by 2015.
We need to get behind this innovation. And to help pay for it, I’m asking Congress to eliminate the billions in taxpayer dollars we currently give to oil companies. I don’t know if you’ve noticed, but they’re doing just fine on their own. So instead of subsidizing yesterday’s energy, let’s invest in tomorrow’s.
Now, clean energy breakthroughs will only translate into clean energy jobs if businesses know there will be a market for what they’re selling. So tonight, I challenge you to join me in setting a new goal: by 2035, 80% of America’s electricity will come from clean energy sources. Some folks want wind and solar. Others want nuclear, clean coal, and natural gas. To meet this goal, we will need them all – and I urge Democrats and Republicans to work together to make it happen.
Maintaining our leadership in research and technology is crucial to America’s success. But if we want to win the future – if we want innovation to produce jobs in America and not overseas – then we also have to win the race to educate our kids.
Think about it. Over the next ten years, nearly half of all new jobs will require education that goes beyond a high school degree. And yet, as many as a quarter of our students aren’t even finishing high school. The quality of our math and science education lags behind many other nations. America has fallen to 9th in the proportion of young people with a college degree. And so the question is whether all of us – as citizens, and as parents – are willing to do what’s necessary to give every child a chance to succeed.
That responsibility begins not in our classrooms, but in our homes and communities. It’s family that first instills the love of learning in a child. Only parents can make sure the TV is turned off and homework gets done. We need to teach our kids that it’s not just the winner of the Super Bowl who deserves to be celebrated, but the winner of the science fair; that success is not a function of fame or PR, but of hard work and discipline.
Our schools share this responsibility. When a child walks into a classroom, it should be a place of high expectations and high performance. But too many schools don’t meet this test. That’s why instead of just pouring money into a system that’s not working, we launched a competition called Race to the Top. To all fifty states, we said, “If you show us the most innovative plans to improve teacher quality and student achievement, we’ll show you the money.”
Race to the Top is the most meaningful reform of our public schools in a generation. For less than one percent of what we spend on education each year, it has led over 40 states to raise their standards for teaching and learning. These standards were developed, not by Washington, but by Republican and Democratic governors throughout the country. And Race to the Top should be the approach we follow this year as we replace No Child Left Behind with a law that is more flexible and focused on what’s best for our kids.
You see, we know what’s possible for our children when reform isn’t just a top-down mandate, but the work of local teachers and principals; school boards and communities.
Take a school like Bruce Randolph in Denver. Three years ago, it was rated one of the worst schools in Colorado; located on turf between two rival gangs. But last May, 97% of the seniors received their diploma. Most will be the first in their family to go to college. And after the first year of the school’s transformation, the principal who made it possible wiped away tears when a student said “Thank you, Mrs. Waters, for showing… that we are smart and we can make it.”
Let’s also remember that after parents, the biggest impact on a child’s success comes from the man or woman at the front of the classroom. In South Korea, teachers are known as “nation builders.” Here in America, it’s time we treated the people who educate our children with the same level of respect. We want to reward good teachers and stop making excuses for bad ones. And over the next ten years, with so many Baby Boomers retiring from our classrooms, we want to prepare 100,000 new teachers in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and math.
In fact, to every young person listening tonight who’s contemplating their career choice: If you want to make a difference in the life of our nation; if you want to make a difference in the life of a child – become a teacher. Your country needs you.
Of course, the education race doesn’t end with a high school diploma. To compete, higher education must be within reach of every American. That’s why we’ve ended the unwarranted taxpayer subsidies that went to banks, and used the savings to make college affordable for millions of students. And this year, I ask Congress to go further, and make permanent our tuition tax credit – worth $10,000 for four years of college.
Because people need to be able to train for new jobs and careers in today’s fast-changing economy, we are also revitalizing America’s community colleges. Last month, I saw the promise of these schools at Forsyth Tech in North Carolina. Many of the students there used to work in the surrounding factories that have since left town. One mother of two, a woman named Kathy Proctor, had worked in the furniture industry since she was 18 years old. And she told me she’s earning her degree in biotechnology now, at 55 years old, not just because the furniture jobs are gone, but because she wants to inspire her children to pursue their dreams too. As Kathy said, “I hope it tells them to never give up.”
If we take these steps – if we raise expectations for every child, and give them the best possible chance at an education, from the day they’re born until the last job they take – we will reach the goal I set two years ago: by the end of the decade, America will once again have the highest proportion of college graduates in the world.
One last point about education. Today, there are hundreds of thousands of students excelling in our schools who are not American citizens. Some are the children of undocumented workers, who had nothing to do with the actions of their parents. They grew up as Americans and pledge allegiance to our flag, and yet live every day with the threat of deportation. Others come here from abroad to study in our colleges and universities. But as soon as they obtain advanced degrees, we send them back home to compete against us. It makes no sense.
Now, I strongly believe that we should take on, once and for all, the issue of illegal immigration. I am prepared to work with Republicans and Democrats to protect our borders, enforce our laws and address the millions of undocumented workers who are now living in the shadows. I know that debate will be difficult and take time. But tonight, let’s agree to make that effort. And let’s stop expelling talented, responsible young people who can staff our research labs, start new businesses, and further enrich this nation.
The third step in winning the future is rebuilding America. To attract new businesses to our shores, we need the fastest, most reliable ways to move people, goods, and information – from high-speed rail to high-speed internet.
Our infrastructure used to be the best – but our lead has slipped. South Korean homes now have greater internet access than we do. Countries in Europe and Russia invest more in their roads and railways than we do. China is building faster trains and newer airports. Meanwhile, when our own engineers graded our nation’s infrastructure, they gave us a “D.”
We have to do better. America is the nation that built the transcontinental railroad, brought electricity to rural communities, and constructed the interstate highway system. The jobs created by these projects didn’t just come from laying down tracks or pavement. They came from businesses that opened near a town’s new train station or the new off-ramp.
Over the last two years, we have begun rebuilding for the 21st century, a project that has meant thousands of good jobs for the hard-hit construction industry. Tonight, I’m proposing that we redouble these efforts.
We will put more Americans to work repairing crumbling roads and bridges. We will make sure this is fully paid for, attract private investment, and pick projects based on what’s best for the economy, not politicians.
Within 25 years, our goal is to give 80% of Americans access to high-speed rail, which could allow you go places in half the time it takes to travel by car. For some trips, it will be faster than flying – without the pat-down. As we speak, routes in California and the Midwest are already underway.
Within the next five years, we will make it possible for business to deploy the next generation of high-speed wireless coverage to 98% of all Americans. This isn’t just about a faster internet and fewer dropped calls. It’s about connecting every part of America to the digital age. It’s about a rural community in Iowa or Alabama where farmers and small business owners will be able to sell their products all over the world. It’s about a firefighter who can download the design of a burning building onto a handheld device; a student who can take classes with a digital textbook; or a patient who can have face-to-face video chats with her doctor.
All these investments – in innovation, education, and infrastructure – will make America a better place to do business and create jobs. But to help our companies compete, we also have to knock down barriers that stand in the way of their success.
Over the years, a parade of lobbyists has rigged the tax code to benefit particular companies and industries. Those with accountants or lawyers to work the system can end up paying no taxes at all. But all the rest are hit with one of the highest corporate tax rates in the world. It makes no sense, and it has to change.
So tonight, I’m asking Democrats and Republicans to simplify the system. Get rid of the loopholes. Level the playing field. And use the savings to lower the corporate tax rate for the first time in 25 years – without adding to our deficit.
To help businesses sell more products abroad, we set a goal of doubling our exports by 2014 – because the more we export, the more jobs we create at home. Already, our exports are up. Recently, we signed agreements with India and China that will support more than 250,000 jobs in the United States. And last month, we finalized a trade agreement with South Korea that will support at least 70,000 American jobs. This agreement has unprecedented support from business and labor; Democrats and Republicans, and I ask this Congress to pass it as soon as possible.
Before I took office, I made it clear that we would enforce our trade agreements, and that I would only sign deals that keep faith with American workers, and promote American jobs. That’s what we did with Korea, and that’s what I intend to do as we pursue agreements with Panama and Colombia, and continue our Asia Pacific and global trade talks.
To reduce barriers to growth and investment, I’ve ordered a review of government regulations. When we find rules that put an unnecessary burden on businesses, we will fix them. But I will not hesitate to create or enforce commonsense safeguards to protect the American people. That’s what we’ve done in this country for more than a century. It’s why our food is safe to eat, our water is safe to drink, and our air is safe to breathe. It’s why we have speed limits and child labor laws. It’s why last year, we put in place consumer protections against hidden fees and penalties by credit card companies, and new rules to prevent another financial crisis. And it’s why we passed reform that finally prevents the health insurance industry from exploiting patients.
Now, I’ve heard rumors that a few of you have some concerns about the new health care law. So let me be the first to say that anything can be improved. If you have ideas about how to improve this law by making care better or more affordable, I am eager to work with you. We can start right now by correcting a flaw in the legislation that has placed an unnecessary bookkeeping burden on small businesses.
What I’m not willing to do is go back to the days when insurance companies could deny someone coverage because of a pre-existing condition. I’m not willing to tell James Howard, a brain cancer patient from Texas, that his treatment might not be covered. I’m not willing to tell Jim Houser, a small business owner from Oregon, that he has to go back to paying $5,000 more to cover his employees. As we speak, this law is making prescription drugs cheaper for seniors and giving uninsured students a chance to stay on their parents’ coverage. So instead of re-fighting the battles of the last two years, let’s fix what needs fixing and move forward.
Now, the final step – a critical step – in winning the future is to make sure we aren’t buried under a mountain of debt.
We are living with a legacy of deficit-spending that began almost a decade ago. And in the wake of the financial crisis, some of that was necessary to keep credit flowing, save jobs, and put money in people’s pockets.
But now that the worst of the recession is over, we have to confront the fact that our government spends more than it takes in. That is not sustainable. Every day, families sacrifice to live within their means. They deserve a government that does the same.
So tonight, I am proposing that starting this year, we freeze annual domestic spending for the next five years. This would reduce the deficit by more than $400 billion over the next decade, and will bring discretionary spending to the lowest share of our economy since Dwight Eisenhower was president.
This freeze will require painful cuts. Already, we have frozen the salaries of hardworking federal employees for the next two years. I’ve proposed cuts to things I care deeply about, like community action programs. The Secretary of Defense has also agreed to cut tens of billions of dollars in spending that he and his generals believe our military can do without.
I recognize that some in this Chamber have already proposed deeper cuts, and I’m willing to eliminate whatever we can honestly afford to do without. But let’s make sure that we’re not doing it on the backs of our most vulnerable citizens. And let’s make sure what we’re cutting is really excess weight. Cutting the deficit by gutting our investments in innovation and education is like lightening an overloaded airplane by removing its engine. It may feel like you’re flying high at first, but it won’t take long before you’ll feel the impact.
Now, most of the cuts and savings I’ve proposed only address annual domestic spending, which represents a little more than 12% of our budget. To make further progress, we have to stop pretending that cutting this kind of spending alone will be enough. It won’t.
The bipartisan Fiscal Commission I created last year made this crystal clear. I don’t agree with all their proposals, but they made important progress. And their conclusion is that the only way to tackle our deficit is to cut excessive spending wherever we find it – in domestic spending, defense spending, health care spending, and spending through tax breaks and loopholes.
This means further reducing health care costs, including programs like Medicare and Medicaid, which are the single biggest contributor to our long-term deficit. Health insurance reform will slow these rising costs, which is part of why nonpartisan economists have said that repealing the health care law would add a quarter of a trillion dollars to our deficit. Still, I’m willing to look at other ideas to bring down costs, including one that Republicans suggested last year: medical malpractice reform to rein in frivolous lawsuits.
To put us on solid ground, we should also find a bipartisan solution to strengthen Social Security for future generations. And we must do it without putting at risk current retirees, the most vulnerable, or people with disabilities; without slashing benefits for future generations; and without subjecting Americans’ guaranteed retirement income to the whims of the stock market.
And if we truly care about our deficit, we simply cannot afford a permanent extension of the tax cuts for the wealthiest 2% of Americans. Before we take money away from our schools, or scholarships away from our students, we should ask millionaires to give up their tax break.
It’s not a matter of punishing their success. It’s about promoting America’s success.
In fact, the best thing we could do on taxes for all Americans is to simplify the individual tax code. This will be a tough job, but members of both parties have expressed interest in doing this, and I am prepared to join them.
So now is the time to act. Now is the time for both sides and both houses of Congress – Democrats and Republicans – to forge a principled compromise that gets the job done. If we make the hard choices now to rein in our deficits, we can make the investments we need to win the future.
Let me take this one step further. We shouldn’t just give our people a government that’s more affordable. We should give them a government that’s more competent and efficient. We cannot win the future with a government of the past.
We live and do business in the information age, but the last major reorganization of the government happened in the age of black and white TV. There are twelve different agencies that deal with exports. There are at least five different entities that deal with housing policy. Then there’s my favorite example: the Interior Department is in charge of salmon while they’re in fresh water, but the Commerce Department handles them in when they’re in saltwater. And I hear it gets even more complicated once they’re smoked.
Now, we have made great strides over the last two years in using technology and getting rid of waste. Veterans can now download their electronic medical records with a click of the mouse. We’re selling acres of federal office space that hasn’t been used in years, and we will cut through red tape to get rid of more. But we need to think bigger. In the coming months, my administration will develop a proposal to merge, consolidate, and reorganize the federal government in a way that best serves the goal of a more competitive America. I will submit that proposal to Congress for a vote – and we will push to get it passed.
In the coming year, we will also work to rebuild people’s faith in the institution of government. Because you deserve to know exactly how and where your tax dollars are being spent, you will be able to go to a website and get that information for the very first time in history. Because you deserve to know when your elected officials are meeting with lobbyists, I ask Congress to do what the White House has already done: put that information online. And because the American people deserve to know that special interests aren’t larding up legislation with pet projects, both parties in Congress should know this: if a bill comes to my desk with earmarks inside, I will veto it.
A 21st century government that’s open and competent. A government that lives within its means. An economy that’s driven by new skills and ideas. Our success in this new and changing world will require reform, responsibility, and innovation. It will also require us to approach that world with a new level of engagement in our foreign affairs.
Just as jobs and businesses can now race across borders, so can new threats and new challenges. No single wall separates East and West; no one rival superpower is aligned against us.
And so we must defeat determined enemies wherever they are, and build coalitions that cut across lines of region and race and religion. America’s moral example must always shine for all who yearn for freedom, justice, and dignity. And because we have begun this work, tonight we can say that American leadership has been renewed and America’s standing has been restored.
Look to Iraq, where nearly 100,000 of our brave men and women have left with their heads held high; where American combat patrols have ended; violence has come down; and a new government has been formed. This year, our civilians will forge a lasting partnership with the Iraqi people, while we finish the job of bringing our troops out of Iraq. America’s commitment has been kept; the Iraq War is coming to an end.
Of course, as we speak, al Qaeda and their affiliates continue to plan attacks against us. Thanks to our intelligence and law enforcement professionals, we are disrupting plots and securing our cities and skies. And as extremists try to inspire acts of violence within our borders, we are responding with the strength of our communities, with respect for the rule of law, and with the conviction that American Muslims are a part of our American family.
We have also taken the fight to al Qaeda and their allies abroad. In Afghanistan, our troops have taken Taliban strongholds and trained Afghan Security Forces. Our purpose is clear – by preventing the Taliban from reestablishing a stranglehold over the Afghan people, we will deny al Qaeda the safe-haven that served as a launching pad for 9/11.
Thanks to our heroic troops and civilians, fewer Afghans are under the control of the insurgency. There will be tough fighting ahead, and the Afghan government will need to deliver better governance. But we are strengthening the capacity of the Afghan people and building an enduring partnership with them. This year, we will work with nearly 50 countries to begin a transition to an Afghan lead. And this July, we will begin to bring our troops home.
In Pakistan, al Qaeda’s leadership is under more pressure than at any point since 2001. Their leaders and operatives are being removed from the battlefield. Their safe-havens are shrinking. And we have sent a message from the Afghan border to the Arabian Peninsula to all parts of the globe: we will not relent, we will not waver, and we will defeat you.
American leadership can also be seen in the effort to secure the worst weapons of war. Because Republicans and Democrats approved the New START Treaty, far fewer nuclear weapons and launchers will be deployed. Because we rallied the world, nuclear materials are being locked down on every continent so they never fall into the hands of terrorists.
Because of a diplomatic effort to insist that Iran meet its obligations, the Iranian government now faces tougher and tighter sanctions than ever before. And on the Korean peninsula, we stand with our ally South Korea, and insist that North Korea keeps its commitment to abandon nuclear weapons.
This is just a part of how we are shaping a world that favors peace and prosperity. With our European allies, we revitalized NATO, and increased our cooperation on everything from counter-terrorism to missile defense. We have reset our relationship with Russia, strengthened Asian alliances, and built new partnerships with nations like India. This March, I will travel to Brazil, Chile, and El Salvador to forge new alliances for progress in the Americas. Around the globe, we are standing with those who take responsibility – helping farmers grow more food; supporting doctors who care for the sick; and combating the corruption that can rot a society and rob people of opportunity.
Recent events have shown us that what sets us apart must not just be our power – it must be the purpose behind it. In South Sudan – with our assistance – the people were finally able to vote for independence after years of war. Thousands lined up before dawn. People danced in the streets. One man who lost four of his brothers at war summed up the scene around him: “This was a battlefield for most of my life. Now we want to be free.”
We saw that same desire to be free in Tunisia, where the will of the people proved more powerful than the writ of a dictator. And tonight, let us be clear: the United States of America stands with the people of Tunisia, and supports the democratic aspirations of all people.
We must never forget that the things we’ve struggled for, and fought for, live in the hearts of people everywhere. And we must always remember that the Americans who have borne the greatest burden in this struggle are the men and women who serve our country.
Tonight, let us speak with one voice in reaffirming that our nation is united in support of our troops and their families. Let us serve them as well as they have served us – by giving them the equipment they need; by providing them with the care and benefits they have earned; and by enlisting our veterans in the great task of building our own nation.
Our troops come from every corner of this country – they are black, white, Latino, Asian and Native American. They are Christian and Hindu, Jewish and Muslim. And, yes, we know that some of them are gay. Starting this year, no American will be forbidden from serving the country they love because of who they love. And with that change, I call on all of our college campuses to open their doors to our military recruiters and the ROTC. It is time to leave behind the divisive battles of the past. It is time to move forward as one nation.
We should have no illusions about the work ahead of us. Reforming our schools; changing the way we use energy; reducing our deficit – none of this is easy. All of it will take time. And it will be harder because we will argue about everything. The cost. The details. The letter of every law.
Of course, some countries don’t have this problem. If the central government wants a railroad, they get a railroad – no matter how many homes are bulldozed. If they don’t want a bad story in the newspaper, it doesn’t get written.
And yet, as contentious and frustrating and messy as our democracy can sometimes be, I know there isn’t a person here who would trade places with any other nation on Earth.
We may have differences in policy, but we all believe in the rights enshrined in our Constitution. We may have different opinions, but we believe in the same promise that says this is a place where you can make it if you try. We may have different backgrounds, but we believe in the same dream that says this is a country where anything’s possible. No matter who you are. No matter where you come from.
That dream is why I can stand here before you tonight. That dream is why a working class kid from Scranton can stand behind me. That dream is why someone who began by sweeping the floors of his father’s Cincinnati bar can preside as Speaker of the House in the greatest nation on Earth.
That dream – that American Dream – is what drove the Allen Brothers to reinvent their roofing company for a new era. It’s what drove those students at Forsyth Tech to learn a new skill and work towards the future. And that dream is the story of a small business owner named Brandon Fisher.
Brandon started a company in Berlin, Pennsylvania that specializes in a new kind of drilling technology. One day last summer, he saw the news that halfway across the world, 33 men were trapped in a Chilean mine, and no one knew how to save them.
But Brandon thought his company could help. And so he designed a rescue that would come to be known as Plan B. His employees worked around the clock to manufacture the necessary drilling equipment. And Brandon left for Chile.
Along with others, he began drilling a 2,000 foot hole into the ground, working three or four days at a time with no sleep. Thirty-seven days later, Plan B succeeded, and the miners were rescued. But because he didn’t want all of the attention, Brandon wasn’t there when the miners emerged. He had already gone home, back to work on his next project.
Later, one of his employees said of the rescue, “We proved that Center Rock is a little company, but we do big things.”
We do big things.
From the earliest days of our founding, America has been the story of ordinary people who dare to dream. That’s how we win the future.
We are a nation that says, “I might not have a lot of money, but I have this great idea for a new company. I might not come from a family of college graduates, but I will be the first to get my degree. I might not know those people in trouble, but I think I can help them, and I need to try. I’m not sure how we’ll reach that better place beyond the horizon, but I know we’ll get there. I know we will.”
We do big things.
The idea of America endures. Our destiny remains our choice. And tonight, more than two centuries later, it is because of our people that our future is hopeful, our journey goes forward, and the state of our union is strong.
Thank you, God Bless You, and may God Bless the United States of America.













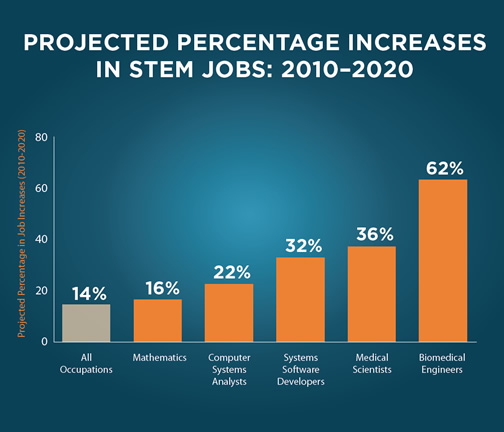







 Less than 20% of engineering bachelor degrees currently go to women and recent trends have been declining. Reports from the National Academy of Engineering and National Research Council explore the challenges the nation currently faces in developing a strong and diverse workforce. All are free to download.
Less than 20% of engineering bachelor degrees currently go to women and recent trends have been declining. Reports from the National Academy of Engineering and National Research Council explore the challenges the nation currently faces in developing a strong and diverse workforce. All are free to download.











































 Rising Above the Gathering Storm
Rising Above the Gathering Storm

 The Dragon and the Elephant: Understanding the Development of Innovation Capacity in China and India
The Dragon and the Elephant: Understanding the Development of Innovation Capacity in China and India
















 Ready, Set, SCIENCE!
Ready, Set, SCIENCE!
 Expanding Under-represented Minority Participation: America’s Science and Technology Talent at the Crossroads
Expanding Under-represented Minority Participation: America’s Science and Technology Talent at the Crossroads How Students Learn
How Students Learn Mathematics Learning in Early Childhood
Mathematics Learning in Early Childhood Adding It Up: Helping Children Learn Mathematics
Adding It Up: Helping Children Learn Mathematics