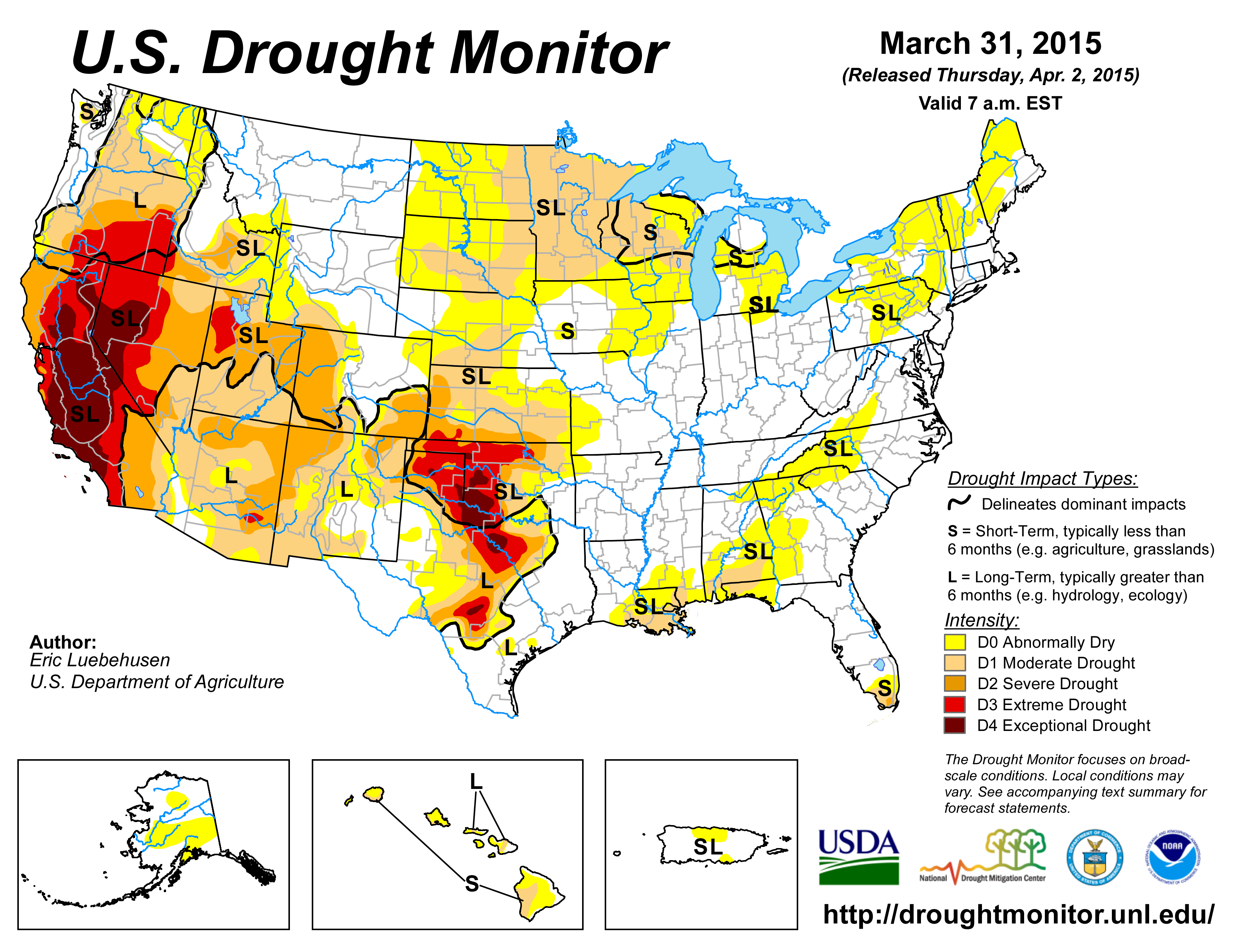
Last week, California’s Governor Jerry Brown announced the first mandatory water restrictions in the state’s history. After four years of drought, the state is being challenged to cut water output by 25 percent while meeting the competing water needs of residents, industry, and agriculture. This image from the National Drought Mitigation Center shows the severity of the drought.
What options do states and communities have to increase the supply of usable water and protect the environment? Reports from the National Research Council explore water management, water reuse, and environmental management. All are free to download.
Expanding water reuse–the use of treated wastewater for beneficial purposes including irrigation, industrial uses, and drinking water augmentation–could significantly increase the nation’s total available water resources. Water Reuse …
In communities all around the world, water supplies are coming under increasing pressure as population growth, climate change, pollution, and changes in land use affect water quantity and quality. To address existing and anticipated water …
There has been an exponential increase in desalination capacity both globally and nationally since 1960, fueled in part by growing concern for local water scarcity and made possible to a great extent by a major federal investment for desalination …
Growing demands for water in many parts of the nation are fueling the search for new approaches to sustainable water management, including how best to store water. Society has historically relied on dams and reservoirs, but problems such as high …
Extensively modified over the last century and a half, California’s San Francisco Bay Delta Estuary remains biologically diverse and functions as a central element in California’s water supply system. Uncertainties about the future, actions …
Water is our most fundamental natural resource, a resource that is limited. Challenges to our nation’s water resources continue to grow, driven by population growth, ecological needs, climate change, and other pressures. The nation needs more and …
The San Francisco Bay Delta Estuary is a large, complex estuarine ecosystem in California. It has been substantially altered by dikes, levees, channelization, pumps, human development, introduced species, dams on its tributary streams and …
California’s Bay-Delta estuary is a biologically diverse estuarine ecosystem that plays a central role in the distribution of California’s water from the state’s wetter northern regions to its southern, arid, and populous cities and agricultural …
Nutrient recycling, habitat for plants and animals, flood control, and water supply are among the many beneficial services provided by aquatic ecosystems. In making decisions about human activities, such as draining a wetland for a housing …
Recent studies of past climate and streamflow conditions have broadened understanding of long-term water availability in the Colorado River, revealing many periods when streamflow was lower than at any time in the past 100 years of recorded …









